Health Belief Model Lung Cancer
The aim of investigation is to explore the relationship between demands for lung cancer screening LCS and the constructs derived from the health belief model HBM in Hefei. Since then there have been a number of reminder campaigns to keep the key messages front of mind.
Perceived greater risks of smoking for cancer prognosis more severe health effects from smoking fewer benefits of smoking and greater social pressure to quit.
Health belief model lung cancer. It was piloted regionally from October to November 2011 and went national for the first time in May 2012. As the Health Belief Model 8 the Theory of Planned Be-havior 9 and the Cognitive-Social Health Information-. Content analysis was performed to identify themes of knowledge and beliefs about lung cancer associated risk factors and lung cancer screening among long-term smokers who had and had not been screened for lung cancer.
The health belief models associations with colorectal cancer screening uptake was consistent with preventive health behaviours in general. The model is based on the theory that a persons willingness to change their health behaviors is. Tobacco users perceived chances of developing smoking-related conditions ie lung cancer CVD gum disease infertility etc.
Abstract The aim of investigation is to explore the relationship between demands for lung cancer screening LCS and the constructs derived from the health belief model HBM in Hefei. They strongly believed that they had a high chance. These findings should provide the impetus for enhanced patient-provider communication that elicits patients beliefs.
Thirteen percent perceived themselves as more susceptible to lung cancer than others of their same age and sex though one in five believed that low SES people were more likely to develop lung cancer than higher SES people. Methods Twenty-six long-term smokers were recruited. Lung and head-and-neck cancers which are strongly asso-.
Then it is necessary to feel threatened by these perceptions. Cancer survivors are able to undergo treatment with family social support. A person must evaluate their perceptions of susceptibility and severity of developing a disease.
The study collected data about socio-demographics health beliefs in and demands for LCS during early June to. The Health Belief Model HBM served as the theoretical basis for developing the conceptual framework of this study. Twenty-five percent believed that almost everyone who develops lung cancer dies of it within five years of diagnosis.
Therefore the objective of this study is to assess public awareness perceptions and intention to use genetic testing for the susceptibility to lung cancer as well as identifying the factors which may affect intention to use a genetic test to screen for lung cancer risk. The Health Belief Model HBM is a tool that scientists use to try and predict health behaviors. The purpose of this literature review is to characterize unconventional health beliefs and complementary and alternative medicine CAM for asthma smoking and lung cancer as those that are likely safe and those that likely increase risk in diverse Black communities.
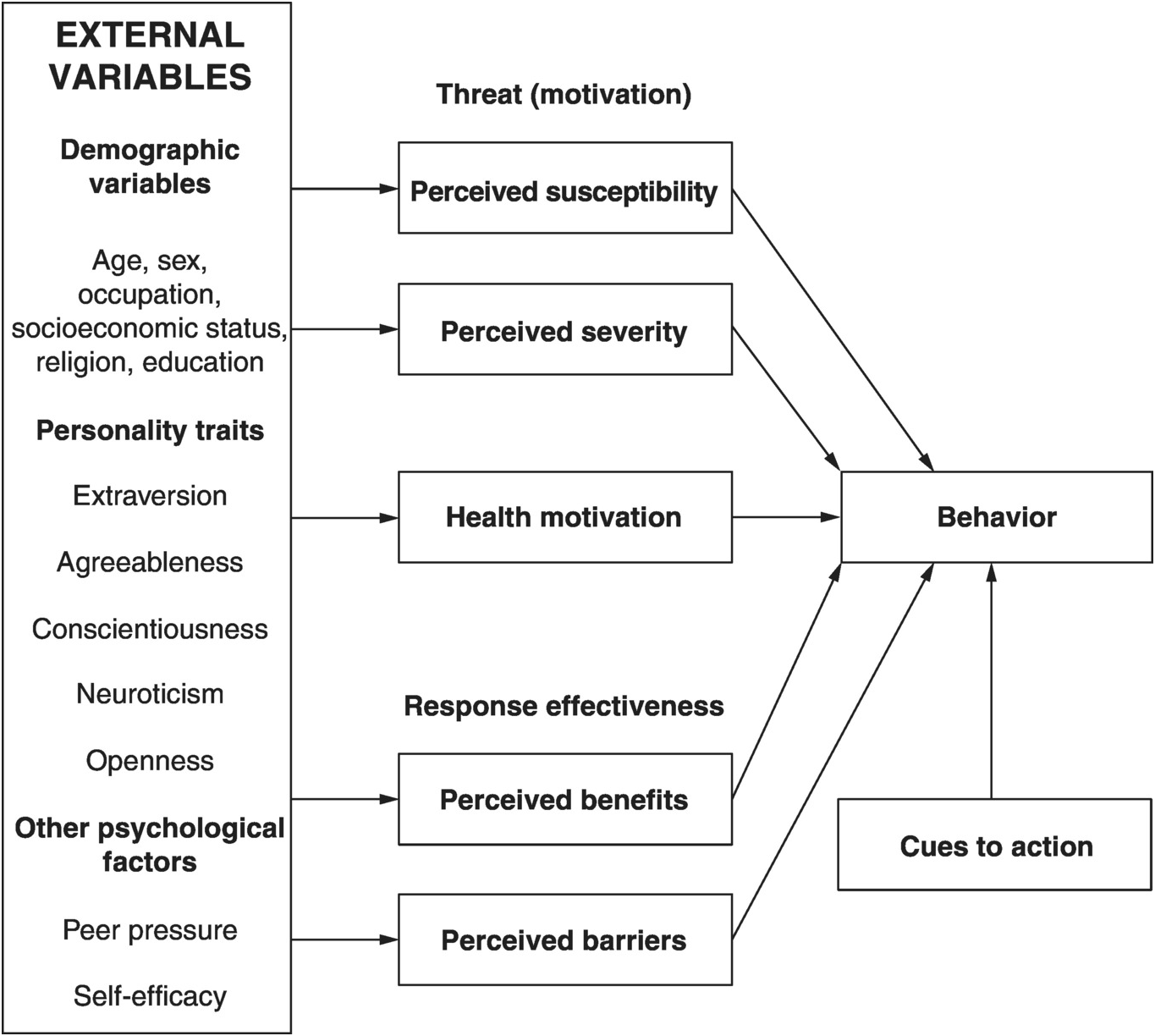
The Be Clear on Cancer brand has been used to promote awareness and early diagnosis of lung cancer since 2010. Future studies should examine how theory-based behavioural interventions can be tailored to account for the influence of socioecological factors. Key constructs in the Health Belief Model include perceived risks and benefits with regard to tobacco use perceived barriers and self-efficacy for quitting and cues to action see table below.
ConclusionThe Health Belief Model is a simultaneous process used to encourage healthy behavior among individuals who put themselves at risk of developing negative health outcomes. 19 Cues to action are referred to as factors to trigger individuals to behave healthy. Health Belief Model based on four focus group discussions.
The study collected data about socio-demographics health beliefs in and demands for LCS during early June to. The Health Belief Model stated that cues triggers are needed to encourage engagement in health-promoting behavior. HEALTH BELIEF MODEL HBM Rosenstock1966 Becker 1970 1980 HBM first proposed by Rosenstock 1966 and then refined by Becker et al 1970 and 1980 HBM is used to predict preventive health behavior and behavioral responses to the treatment of patients with acute and chronic diseases.
The HBM has been tested translated and. Participants strongly believed that if they did not stop smoking they were at high risk of lung cancer 88. The Health Belief Model HBM focuses on a persons health-related behavior for predicting future actions 19.
On the health belief model showed that 1 perceived susceptibility. The Lung Cancer Screening Extended Health Belief Model identified belief in the efficacy of early detection as an important facilitator of screening. Other studies report on the prevalence of a belief in the efficacy of early.
It was originally developed in the 1950s and updated in the 1980s. Cancer of the cervix was the health condition about which there was greatest uncertainty with 288 of respondents unsure whether it could be prevented. Of the three cancers skin cancer was most often rated as all or mostly preventable 617 followed by lung cancer and cancer of the cervix.
Cues to action can be internal or external. 5 Because only one other study has reported a relation between this factor and willingness to screen 31 the current study provides additional empirical support for the model.
Https Scholarscompass Vcu Edu Cgi Viewcontent Cgi Article 5841 Context Etd
Understanding The Decision To Screen For Lung Cancer Or Not A Qualitative Analysis Draucker 2019 Health Expectations Wiley Online Library
Http Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177 216507999003800306
To Know Or Not To Know Push And Pull In Ever Smokers Lung Screening Uptake Decision Making Intentions Tonge 2019 Health Expectations Wiley Online Library
Artificial Intelligence Performance In Detecting Tumor Metastasis From Medical Radiology Imaging A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Eclinicalmedicine
Screening Patterns And Mortality Differences In Patients With Lung Cancer At An Urban Underserved Community Clinical Lung Cancer
The Health Belief Model As Specified By Becker And Maiman X 2 Download Scientific Diagram
Cureus Perception Of Ophthalmologists Of Covid 19 Using The Health Belief Model
Ijerph Free Full Text Structural Factors Affecting Health Examination Behavioral Intention Html
The Use Of Facemasks To Prevent Respiratory Infection A Literature Review In The Context Of The Health Belief Model Abstract Europe Pmc
Understanding Factors Influencing Physical Activity And Exercise In Lung Cancer A Systematic Review Springerlink
Https Www Mdpi Com 2226 4787 9 1 58 Pdf
County Level Variations In Receipt Of Surgery For Early Stage Non Small Cell Lung Cancer In The United States Chest
Ijerph Free Full Text Structural Factors Affecting Health Examination Behavioral Intention Html
Supporting Patients To Make Lifestyle Behaviour Changes
Psychological Aspects Of Health And Illness Section 1 Cambridge Handbook Of Psychology Health And Medicine
Ijerph Free Full Text On The Nature Of Evidence And Proving Causality Smoking And Lung Cancer Vs Sun Exposure Vitamin D And Multiple Sclerosis Html
Health Belief Model An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Posting Komentar untuk "Health Belief Model Lung Cancer"